You can get an accurate landed cost calculation by finding the total cost to ship a product to the buyer.
What is landed cost?
Landed cost is the total expense associated with shipping goods from the source to buyer. This could mean to a buyer’s warehouse or to a customer’s doorstep. You could calculate the landed cost per shipment or per unit. This is an important supply chain KPI in inventory management.
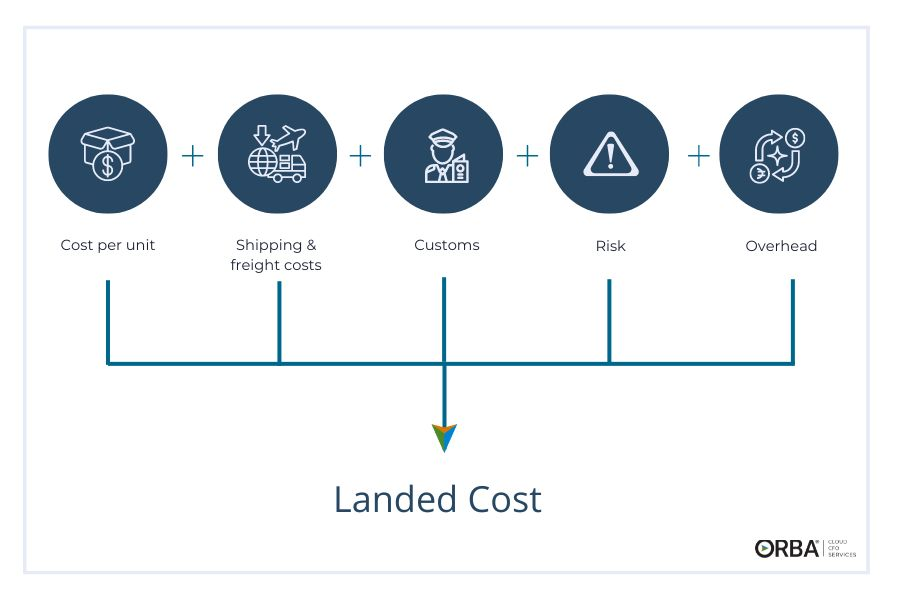
The landed cost formula is:
Landed cost = unit cost of product + shipping/freight costs + customs + risk + overhead
Landed cost reflects direct costs only to move the product from the factory floor to your customer. Sounds simple? There are many external factors that can affect landed cost.
Example of direct costs included in landed cost:
- Manufacturing
- Freight
- Handling costs
- Packaging expenses
- Custom import/export duties
- Currency conversion
- Insurance
- Crating & storage
- Tariffs and Taxes
- All other charges incurred along a product’s transport
Example of indirect costs not included in landed cost:
- Production-related overhead costs
- Cost of labor
- Equipment costs
How to calculate landed cost
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you with your landed cost calculation:
Step 1: Determine the unit cost
The unit cost refers to the price-per-unit of each product.
Step 2: Calculate shipping and freight
Freight costs refer to the cost of transporting the product from the port of origin to the destination port. This includes the cost of shipping, crating, packaging and handling. Consider things like peak holiday fulfillment increases like those we see for FBA in Q4 for example.
Step 3: Calculate customs and duties
Customs refer to the fees charged by the destination country for importing the product. These fees vary depending on the product and the country of origin, but might include duties, tariffs, VAT, broker and harbor or port fees. So, it’s important to research the fees before importing the product. You can use online calculators to estimate the customs and duties for your products.
Step 4: Total the expenses involved in risk
Other costs refer to any additional fees associated with getting the product to the destination. This can include insurance, compliance and quality control expenses.
Step 5: Add in any overhead costs
Finally, add in any overhead costs. These include any special handling, currency conversion, bank fees and payment processing.
Calculating this KPI can seem complex but with proper expense tracking you should be able to determine your accurate price point for the profit margin you’re aiming for. An outsourced controller should be able to help you determine your total landed cost with the right inventory management software.
Why is landed cost important?
Understanding landed cost is important for procurement, pricing and most notable, your profitability. Higher landed costs cuts into savings you might expect from a low per-unit price. Tracking landed costs becomes more important if you’re shipping products internationally when you’re more likely to experience customs, exchange rates and foreign taxes. Three reasons why landed cost is important to supply chain management: procurement, pricing and profitability.
1). Procurement
At first a product that might seem as though it costs less per unit to buy overseas than to purchase it domestically. But factor in things like taxes, insurance and international freight and you might end up spending more. (And waiting longer for your products).
2). Pricing
Understanding landed cost is essential for knowing how to price products. It’s not unusual for us to encounter a new client who has not appropriately accounted for landed cost and therefore does not charge enough to cover their shipping and associated expenses.
3). Profitability
Having a full picture of your landed cost gives your sales team an idea of how much they can discount a product while still bringing in a profit. Your profit margins will diminish with price points that are too low. Tracking your landed cost tells you how much money is going out, which as noted above with pricing, is essential to business planning with your profits. We go into more detail about unit economics in this article about how small businesses lose money. When you have a solid grasp of what the costs of existing products are, you also get a better idea of what percentage of that profit you can use in order to launch a new product or campaign.
Quick tips to improve your landed cost
1). Use an ERP to track your expenses
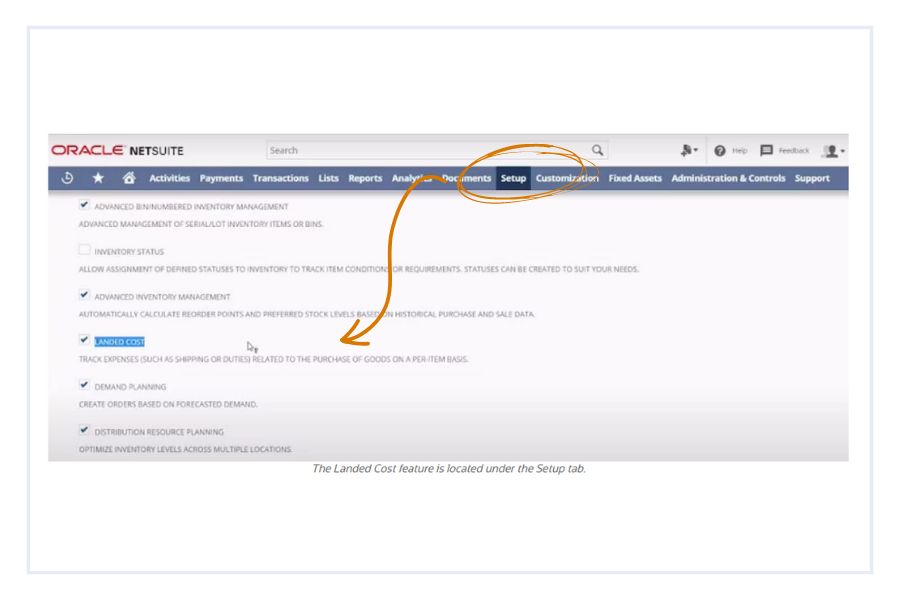
Having the visibility into true costs gives you the full picture of your costs so you can make informed improvements. Automating these calculations saves you time and eventually money. One way to streamline data is by using NetSuite Inventory Management to track expenses and automate your calculation. This increases accuracy and reduces the time-intensive nature of calculating this KPI.
2). Leverage partnerships for discounts
Renegotiate contracts with partners to lower costs. Look for volume-based discounts from manufacturers. Try to lower shipping costs by reducing packaging or carrier costs by sharing loads with other companies near you.
3). Keep inventory lean
One great way to reduce inventory costs is to bundle your deadstock. If you are housing thousands of SKUs you need to know which are the slow sellers to reduce your carrying costs.
4). Add the shipping fees at time of sale or raise your delivery minimum
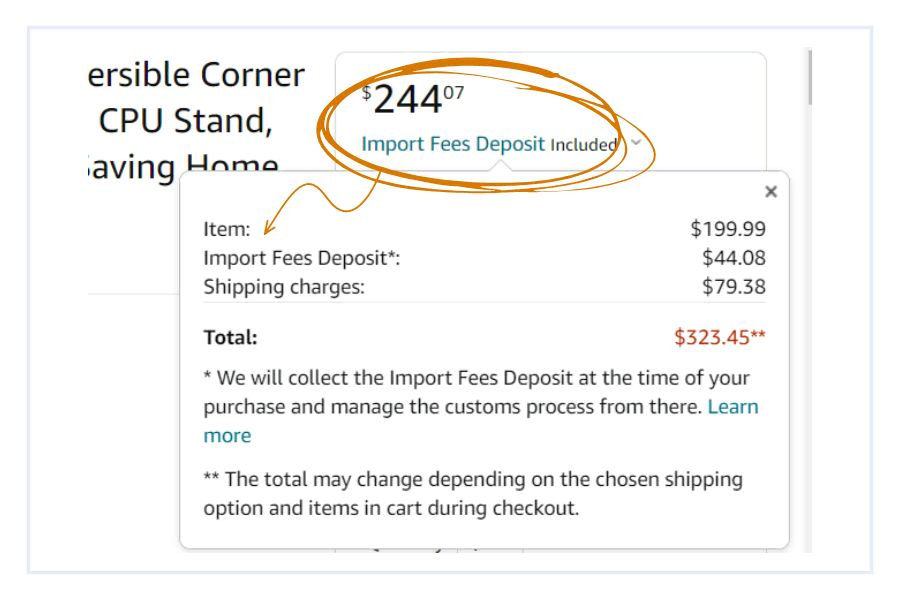
Even customers on Amazon are doing it! Check out the total import and shipping fees added on when you go to checkout for this desk: $123.46!
These additional fees are a little extreme and you don’t want to scare off customers. Be sure to keep any added expenses reasonable for your average customer to avoid sticker shock. If you’re a wholesaler, a smart move is to increase delivery minimums for bigger customers. Keep them happy by offering incentives to order larger quantities.
The Bottom Line
If you’re in the business of consumer products or ecommerce, using an accurate landed cost calculation is essential to optimizing your supply chain and profitability. Need help tracking your landed costs? Get in touch to learn more about our NetSuite bookkeeping services.